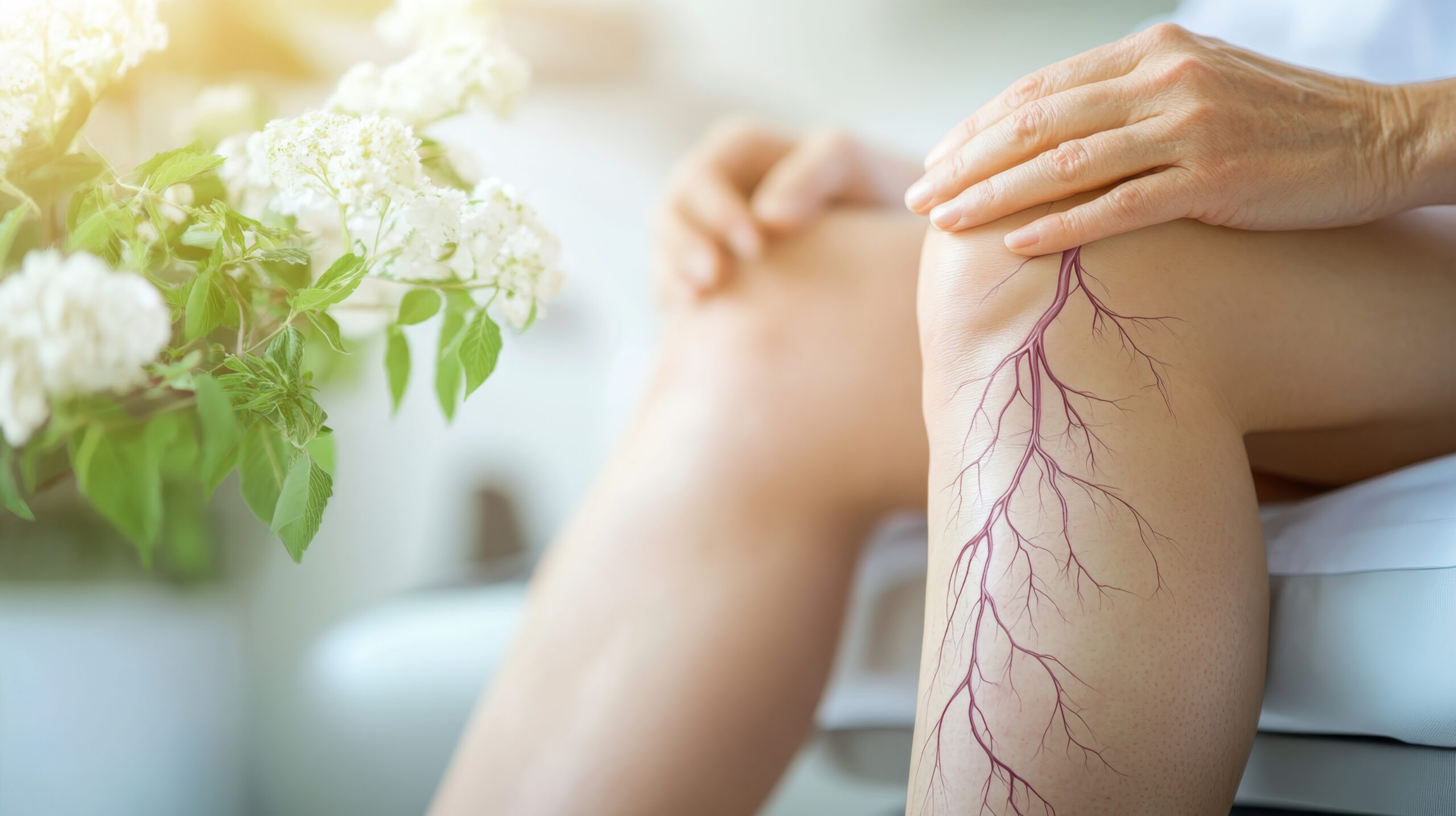
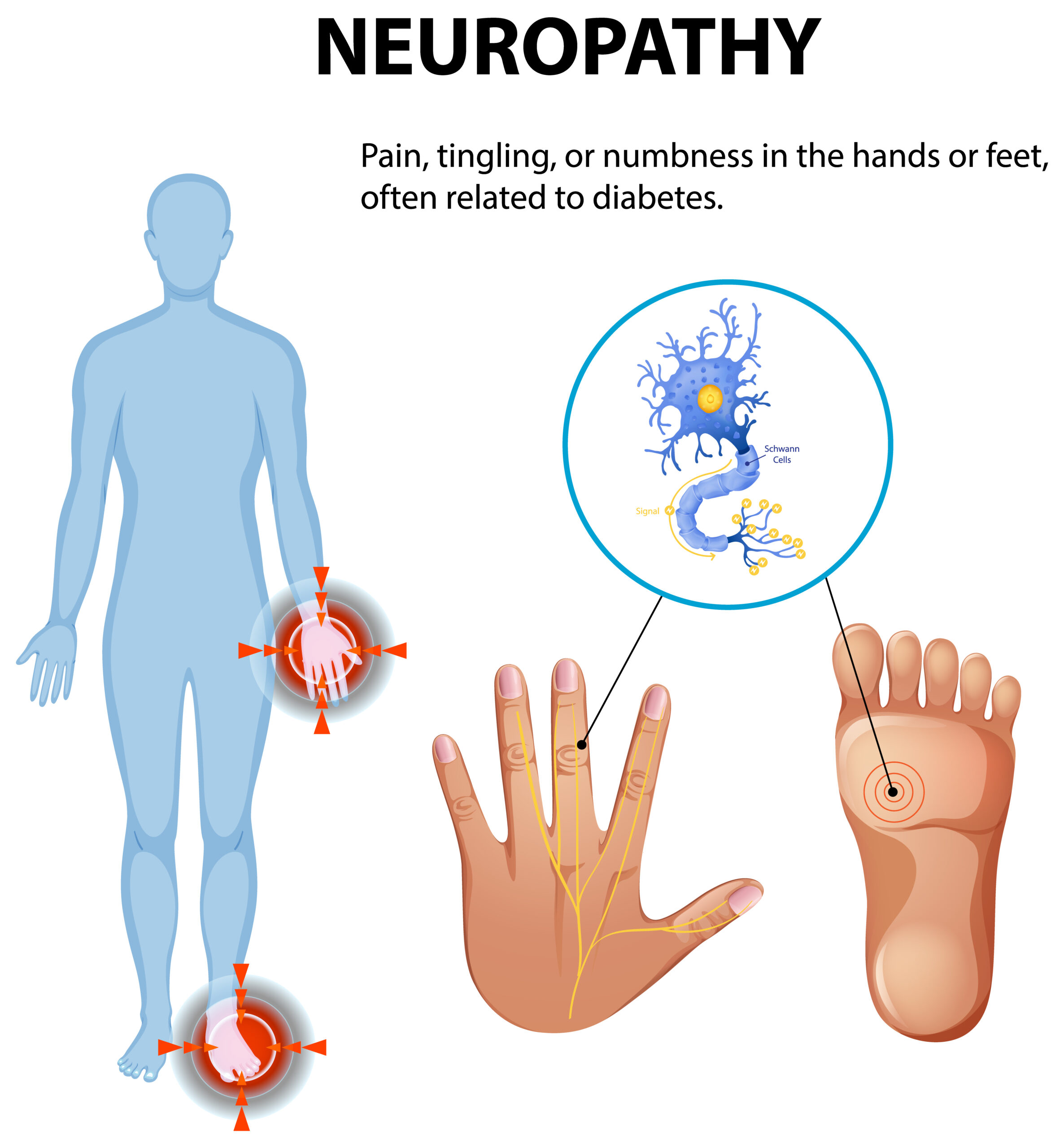
Peripheral neuropathy affects millions worldwide, causing discomfort, weakness, and sensory changes that can significantly impact daily life. But what exactly is peripheral neuropathy, and how can it be managed effectively? Whether you’re experiencing tingling in your feet, burning sensations, or unexplained weakness, understanding this condition is the first step toward relief.
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
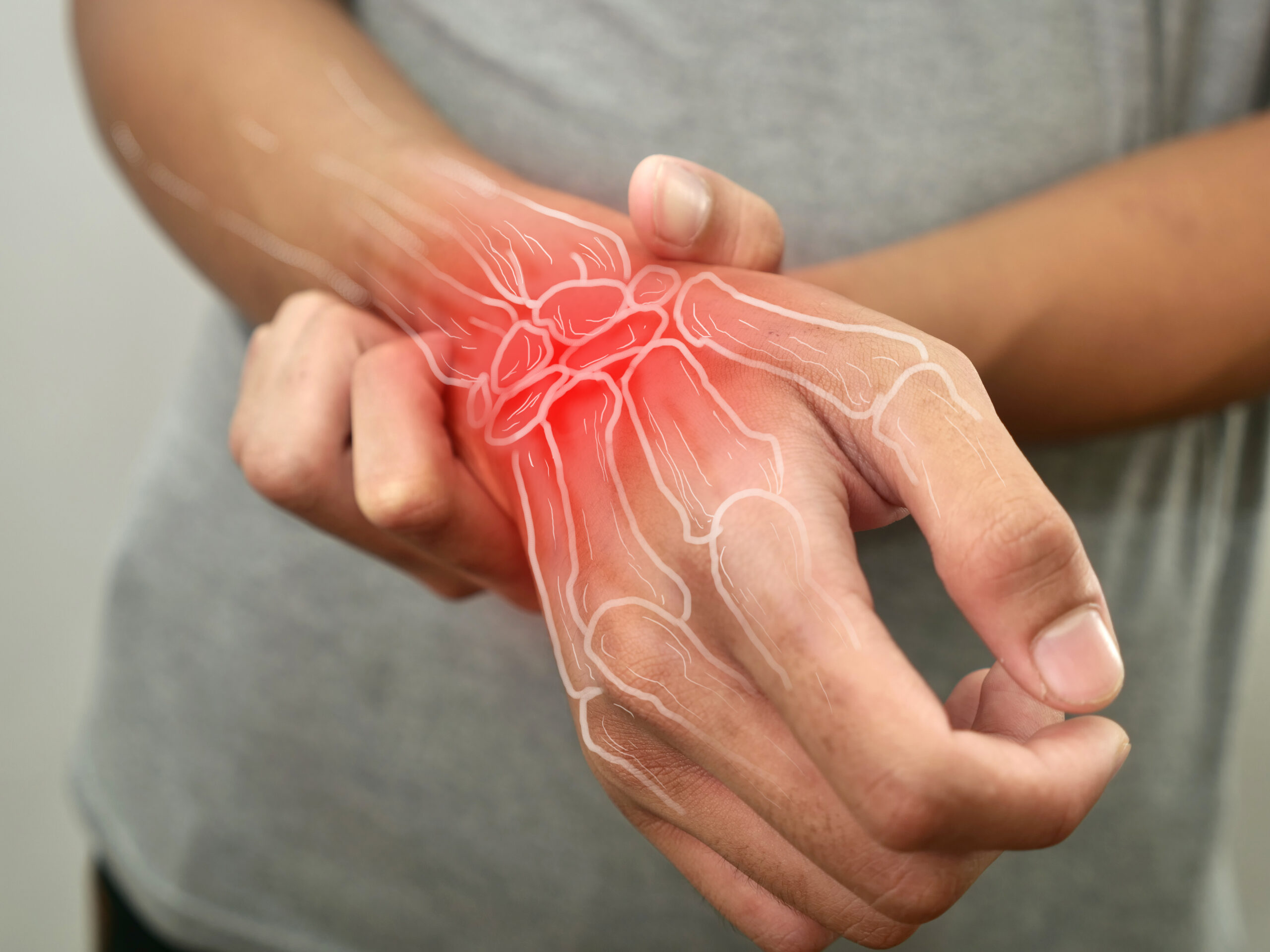
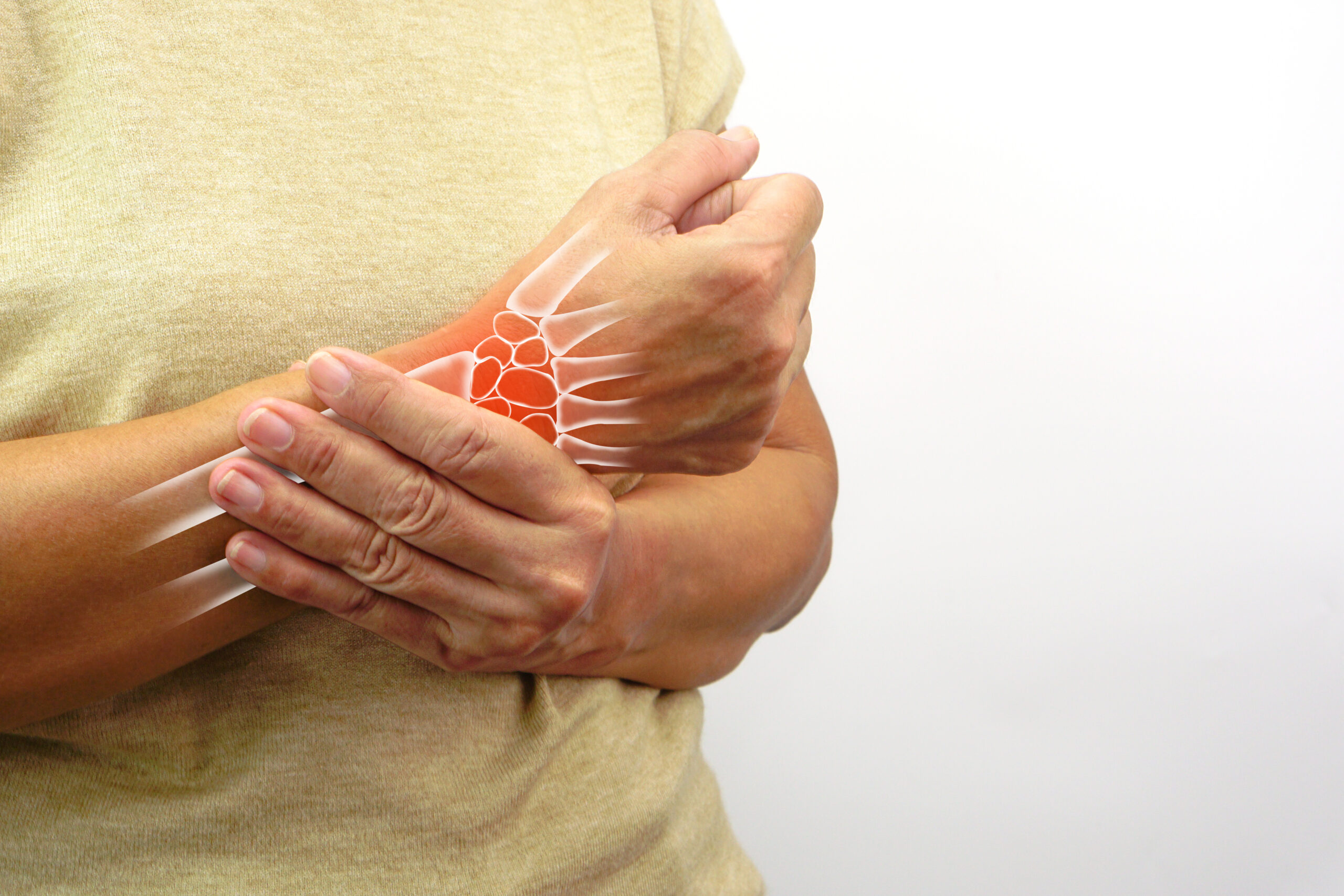
Peripheral neuropathy is a disorder that occurs when the peripheral nerves—the network of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord—are damaged. These nerves are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body.
Damage to these nerves can disrupt communication, leading to pain, numbness, and muscle weakness. The condition can affect a single nerve (mononeuropathy), multiple nerves (multiple mononeuropathy), or many nerves throughout the body (polyneuropathy).
Common Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy can result from a variety of factors, including:
- Diabetes – One of the most common causes; high blood sugar damages nerves over time.
- Infections – Such as shingles, Lyme disease, or HIV.
- Autoimmune diseases – Including lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Vitamin deficiencies – Especially vitamin B12 and folate.
- Alcohol abuse – Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to nerve damage.
- Exposure to toxins – Such as heavy metals or certain medications, especially chemotherapy drugs.
- Injuries – Physical trauma or repetitive stress.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
The symptoms can vary depending on the type of nerves affected:
1. Sensory Nerve Damage
- Tingling or “pins and needles” sensation
- Burning or sharp pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Loss of coordination and balance
2. Motor Nerve Damage
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty walking or performing fine motor skills
- Muscle cramps or twitching
3. Autonomic Nerve Damage
- Blood pressure fluctuations
- Abnormal sweating
- Digestive issues
- Bladder control problems
Types of Peripheral Neuropathy
- Diabetic Neuropathy – Nerve damage due to prolonged high blood sugar.
- Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathy – A side effect of cancer treatments.
- Idiopathic Neuropathy – When the cause is unknown.
- Hereditary Neuropathy – Passed down genetically, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
Diagnosing Peripheral Neuropathy
A healthcare provider will typically:
- Review medical history
- Perform a physical and neurological exam
- Order blood tests to check vitamin levels and blood sugar
- Use nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) to assess nerve function
- In some cases, a nerve biopsy may be performed
Treatment Options for Peripheral Neuropathy
While nerve damage cannot always be reversed, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further damage.
1. Treating the Underlying Cause
- Diabetes management with strict blood sugar control
- Vitamin supplementation for deficiencies
- Adjusting medications if drug-induced
2. Medications
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter NSAIDs or prescription drugs
- Antidepressants: Duloxetine or amitriptyline for nerve pain
- Anti-seizure medications: Gabapentin or pregabalin to calm nerve signals
3. Physical Therapy
- Improves muscle strength and coordination
- Reduces pain and stiffness
4. Lifestyle Changes
- Eating a nutrient-rich diet
- Regular low-impact exercise
- Avoiding alcohol and quitting smoking
Living with Peripheral Neuropathy
Adapting daily habits can significantly improve quality of life:
- Foot Care: Regularly check for injuries, especially in diabetic neuropathy.
- Supportive Shoes: Wear cushioned, well-fitting footwear.
- Assistive Devices: Use canes or braces if mobility is affected.
- Stress Management: Meditation and relaxation techniques can help manage pain perception.
Complications if Left Untreated
- Chronic pain that disrupts sleep and mood
- Increased risk of falls and injuries
- Infections due to unnoticed wounds (especially in the feet)
- Permanent disability in severe cases
Prevention Tips
- Maintain healthy blood sugar levels
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation
- Limit alcohol intake and avoid toxins
- Manage chronic health conditions proactively
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Not always, but treatment can manage symptoms and slow progression.
Recovery depends on the cause and severity—some cases improve within months, while others may be long-term.
Foods rich in B vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants support nerve health.
Yes, low-impact exercise like walking can improve circulation and reduce symptoms.
This varies—many patients benefit from gabapentin, duloxetine, or topical pain relievers.
Peripheral neuropathy can be life-altering, but with the right care and lifestyle adjustments, many people can manage symptoms and maintain a fulfilling life. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing complications.
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately for evaluation and treatment.
Click here to learn more and get specialized care from Asian Vascular Hospitals
Recent Posts
- All Post
- blog
Related posts:
 Trusted Vascular Hospital in Hyderabad: Where Advanced Care Meets Compassion
Trusted Vascular Hospital in Hyderabad: Where Advanced Care Meets Compassion
 Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad: Expert Care to Save Limbs and Lives
Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad: Expert Care to Save Limbs and Lives
 Best Vascular Surgeon Near Me – Expert Care at Asian Vascular Hospitals
Best Vascular Surgeon Near Me – Expert Care at Asian Vascular Hospitals
 Vascular Surgeon Meaning – Who They Are & What They Treat
Vascular Surgeon Meaning – Who They Are & What They Treat
 Surgical Treatment for Varicose Veins – Walk Pain-Free Again
Surgical Treatment for Varicose Veins – Walk Pain-Free Again
 🦶 Diabetic Foot Ulcer – Causes, Risks & Advanced Treatment Options
🦶 Diabetic Foot Ulcer – Causes, Risks & Advanced Treatment Options
 Peripheral Neuropathy Doctors Near Me: How to Find the Right Specialist
Peripheral Neuropathy Doctors Near Me: How to Find the Right Specialist
 Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment: Causes, Options, and Recovery
Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment: Causes, Options, and Recovery